VM Oidium
Erysiphe necator, the pathogen responsible for powdery mildew (Oidium), is a fungal disease that poses a significant threat to viticulture worldwide. Its ability to infect grapevines throughout their growing season makes it one of the most challenging diseases to manage effectively. To assist grape growers in combating this pathogen, we offer a predictive model that evaluates the risk of infection and helps determine the optimal timing for fungicide applications. By focusing on precision, our model supports more efficient use of fungicides, reducing both costs and environmental impact. In this wiki, we will explain the prediction model and where you can find the information to combat oidium.
After a weather station and the tab "Oidium" was selected three different levels of detail of the prediction model for oidium are selectable. The three levels of detail (in ascending order) are Übersicht, Kombiansicht and Detailansicht.

Übersicht
In this tab you find all necessary information in one graph, it should provide an overview of the most important information. In the graph you will find:
- Weather data
- Leaf wetness
- Oidium risk
- Leaf growth

Weather data
Depicted is:
- Humidity (blue line) shows air moisture, which is critical for spore germination.
- Average Temperature (red line) influences the speed of pathogen development.
- Min and max temperature (transparent light red) indicating thresholds for the pathogen
- Precipitation (blue bars) indicates periods when the vine leaves are wet, creating optimal conditions for infection
Leaf wetness
Below the weather data, you will find a bar which indicates leaf wetness (BN). In the "Detailansicht" you can see a more detailed version of this section.
Oidium risk
Colorcoded you will find the risk for an infection with Oidium. We derive the oidium risk based on the OiDiag method.
- Yellow (low risk): infection risk is below 33%
- Orange (medium risk): infection risk is between 34-66%
- Red (high risk): infection risk is above 66%
Leaf growth
We derive our leaf growth model from the "Rebflächenwachstumsmodell" written by Schultz (2003). Depicted in the model is:
- Dark green indicates the total leaf area (in cm²)
- Bright green shows the leaf area which is currently growing
- On the right, you can see a prediction of leaf growth for the upcoming days
Kombiansicht
In this "Kombiansicht" you can find all necessary information to plan plant protection. After you selcted a date that you want to analze, this graph will appear: 
Depicted in the graph is:
- Weather data
- Leaf wetness
- Oidium infection risk
- BBCH-Stage
- Leaf growth model
On the right side of the "Kombiansicht" it is possible to select:
- Info
- Legende
- Phänologie
- Behandlung Wirkungsdauer
Weather data
In the weather data section of the graph, in which you will find:
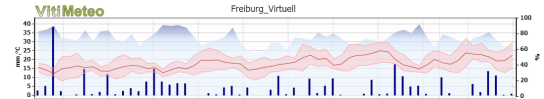
Weather data of the "Kombiansicht"
- Average temperature (red line) influences the speed of pathogen development
- Min/max temperature (light red gradient)
- Precipitation (blue bars) indicates periods when the vine leaves are wet, creating optimal conditions for infection
- Relative humidity (light blue), which is calculated as an average value per day
Leaf wetness

Leaf wetness hours from the Kombiansicht
Below the weather data, you will find a bar which indicates leaf wetness (BN). In the "Detailansicht" you can see a more detailed version of this section.
Oidium infection risk

Oidium infection risk
Is derived from the OiDiag method. Desribed here.
BBCH-Stage

BBCH-stage
Here you can see what our model thinks in which BBCH-stage you vineyard is. Compare the displayed BBCH-stage to your vineyard situation to assess the precision of the model.
Leaf growth model
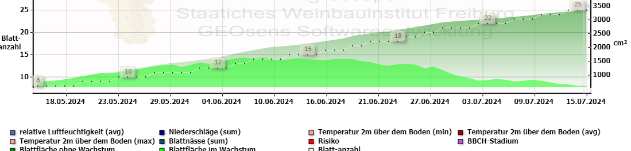
Leaf growth model
We derive our leaf growth model from the "Rebflächenwachstumsmodell" written by Schultz (2003). Depicted in the model is:
- Dark green indicates the total leaf area (in cm²)
- Bright green shows the leaf area which is currently growing
- On the right, you can see a prediction of leaf growth for the upcoming days
Info
Here you can find descriptive papers of how to use our website.
Legende
Describes some elements of the graph.
Phänologie
Here you can select if you want to see the leaf growth model or the BBCH-stages. Furthermore, you can download the generated graph as a picture.
Behandlung Wirkungsdauer
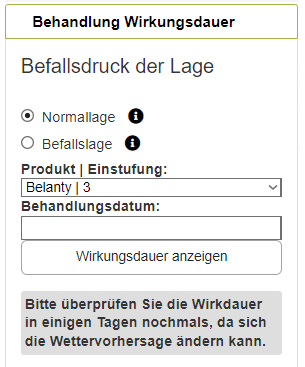
Überschrift
In this section, you will be able to see how long the fungicide of your choice will retain its protective effect. First, select whether you want to analyze a vineyard with or without infections in previous years. If you select "Befallslage," the risk factor will increase accordingly. Next, choose the fungicide you are using and the date it was applied. Click on "Wirkungsdauer anzeigen" to display the duration of protection. A black/grey gradient will appear on the graph, indicating the duration of the protection.
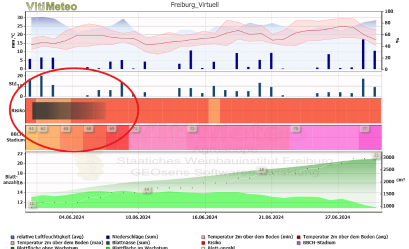
Duration of protection
Detailansicht
The Detailansicht provides an in-depth look at key factors influencing powdery mildew (Oidium) risk. This view is particularly useful for advanced analysis and precise planning, offering detailed data that can guide decisions. Here's what you will find in the Detailansicht:
Weather Data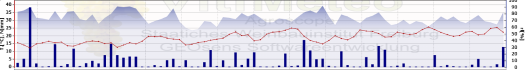
The weather data section offers an hourly breakdown of critical environmental variables:
- Temperature:
- Average (red line): The primary driver of pathogen development speed.
- Min/Max (light red gradient): Highlights temperature thresholds affecting fungal activity.
- Humidity (blue line): Represents hourly air moisture levels, critical for spore germination.
- Precipitation (blue bars): Indicates wet periods that can facilitate infection.
This granular weather data allows for precise identification of infection-prone periods.
Leaf Wetness
- Depicted as a bar chart, showing the number of hours the leaves remain wet (BN) throughout the day.
- Wetness duration correlates directly with fungal spore survival and infection potential.
Use this data to identify extended periods of leaf wetness, which might necessitate additional fungicide applications.
Oidium Infection Risk
- Derived using the OiDiag method, this section provides detailed risk calculations for infection. The higher the oidium index, the higher the risk for an infection.
This precise temporal resolution enables useres to plan dates for application.
Phenology and BBCH Stages
- Displays the model’s estimation of the current BBCH-stage for the vineyard.
- This information helps assess the accuracy of the model against actual growth stages in your vineyard.
Compare these predictions to on-site observations to ensure the model aligns with reality.
Leaf Growth Model 
- Similar to other views, the leaf growth model is included:
- Dark Green: Total leaf area (cm²).
- Bright Green: Actively growing leaf area.
- Growth Predictions: Includes a precise forecast for the coming days.
This level of detail is crucial for timing fungicide applications during rapid growth phases.
How to Use the Detailansicht
- Monitor Hourly Data: Use weather and leaf wetness data to identify periods of heightened infection risk.
- Pinpoint Risk Peaks: Check the Oidium infection risk section to see when risk levels are highest.
- Validate Phenology: Compare BBCH-stage predictions with your observations.
- Adapt to Growth Phases: Utilize leaf growth predictions to schedule fungicide applications more effectively, particularly during fast-growth periods.
The Detailansicht is a powerful tool for those seeking a deeper understanding of vineyard conditions. By using its data, growers can make well-informed decisions that enhance disease management and optimize fungicide use.
