VM Pockenmilbe
Übersicht
Das Pockenmilben-Tool hilft bei der Überwachung des Migrationsrisikos von Pockenmilben (Calepitrimerus vitis) und Blasenmilben (Colomerus vitis). Das Tool nutzt Temperaturdaten zur Vorhersage der Aktivität und ermöglicht es den Nutzern, Behandlungen effektiv zu planen. Dieser Leitfaden erklärt, wie die Diagramme zu interpretieren und zu verwenden sind, um diese Schädlinge im Weinberg zu bekämpfen.
1. Risikoübersicht
Verwendungszweck
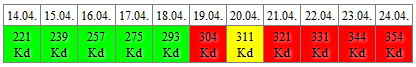
Die Risikoübersichtstabelle enthält Daten über die potenzielle Migration von Pocken- und Blasenmilben. Die wichtigsten Komponenten sind:
- Datumszeile: Grau unterlegte Zellen markieren den Vorhersagezeitraum.
- Temperatursumme (Kelvin-Tage, Kd): Zeigt die Akkumulation der täglichen Durchschnittstemperaturen ab dem 1. März an.
Schwellenwerte
- 300 Kd (Gelb): Migration ist möglich.
- Warme Tage >10°C (Rot): Zeigt wenn Pockenmilben migrieren, zu dieser Zeit ist eine Behandlung mit Insektiziden am effektivsten.
2. Interpretation des Graphs
Die Diagramme beziehen sich auf einen Zeitraum von drei Wochen:
- Zwei Wochen historische Daten
- Der aktuelle Tag
- Der Vorhersagezeitraum
Komponenten des Graphs
Risiko- und Temperaturdaten
- Temperatur-Summenkurve: Zeigt den kumulierten Prozentsatz des Schwellenwerts an.
- Risikobalken: Stellt das Migrationsrisiko anhand von Farben dar, die den in der Legende beschriebenen Schwellenwerten entsprechen.
- Startdatum der Migration: Wird in der Grafik angezeigt, wenn die Bedingungen für die Migration erfüllt sind.
Wetterdaten
- Inkludiert täglichen Durchschnitt für:
- Temperatur
- Niederschlag
- Luftfeuchtigkeit
- Blattnässe
- Inkludiert täglichen Durchschnitt für:
Parameter des Modells
- Der Hintergrund der Temperatursummenkurve ist mit grauen Balken überlagert, die die kumulierten Tagesdurchschnittstemperaturen darstellen.
- Die Grafik zeigt, wann die Migrationsbedingungen zum ersten Mal erfüllt wurden.

3. Praktische Anwendung
Um die Graphen effizient zu nutzen:
- Beobachtung der Temperatursummen: Verfolgen Sie, wann die 300-Kd-Schwelle erreicht wird und warme Tage (>10°C) auftreten.
- Planen der Behandlungen: Planen Sie die Behandlungen während der aktiven Migration (rot markierte Tage), um eine maximale Wirksamkeit zu erzielen.
- Analysieren Sie die Wetterdaten: Bewerten Sie die Umweltbedingungen, um ihre Auswirkungen auf die Milbenaktivität zu bestimmen.
